
 SCIENTIFIC EDUCATION POINT A Concept for Mind Development & Mid Brain Activation |
 A Unit of RGVT, New Delhi [An ISO 9001:2008 Certified Organisation] |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
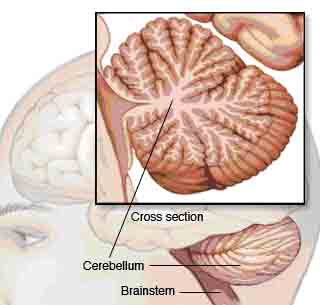 The cerebellum is a wrinkled ball of tissue below and behind the rest of your brain. It works to combine
sensory information from the eyes, ears and muscles to help coordinate movement.
The cerebellum is a wrinkled ball of tissue below and behind the rest of your brain. It works to combine
sensory information from the eyes, ears and muscles to help coordinate movement.The brainstem links the brain to the spinal cord. It controls many functions vital to life, such as heart rate, blood pressure and breathing. This area is also important for sleep. 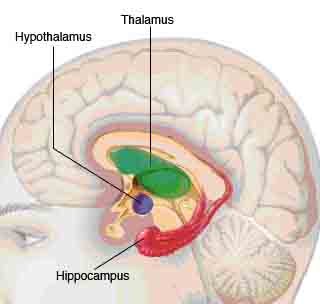 Structures deep within the brain control emotions and memories. Known as the limbic system, these structures
come in pairs. Each part of this system is duplicated in the opposite half of the brain.
Structures deep within the brain control emotions and memories. Known as the limbic system, these structures
come in pairs. Each part of this system is duplicated in the opposite half of the brain.• The thalamus acts as a gatekeeper for messages passed between the spinal cord and the cerebral hemispheres. • The hypothalamus controls emotions. It also regulates your body's temperature and controls crucial urges — such as eating or sleeping. • The hippocampus sends memories to be stored in appropriate sections of the cerebrum and then recalls them when necessary. 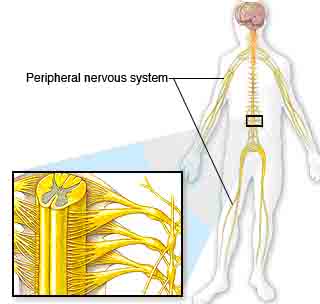 The peripheral nervous system is all the nerves in your body, aside from the ones in your brain and spinal cord.
It acts as a communication relay between your brain and your extremities. For example, if you touch a hot stove,
the pain signals travel from your finger to your brain in a split second. In just as short a time, your brain
tells the muscles in your arm and hand to snatch your finger off the hot stove.
The peripheral nervous system is all the nerves in your body, aside from the ones in your brain and spinal cord.
It acts as a communication relay between your brain and your extremities. For example, if you touch a hot stove,
the pain signals travel from your finger to your brain in a split second. In just as short a time, your brain
tells the muscles in your arm and hand to snatch your finger off the hot stove.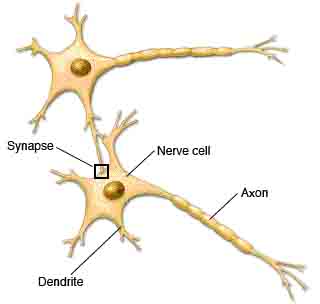 Nerve cells (neurons) have two main types of branches coming off their cell bodies. Dendrites receive incoming
messages from other nerve cells. Axons carry outgoing signals from the cell body to other cells — such as a
nearby neuron or muscle cell.
Nerve cells (neurons) have two main types of branches coming off their cell bodies. Dendrites receive incoming
messages from other nerve cells. Axons carry outgoing signals from the cell body to other cells — such as a
nearby neuron or muscle cell.Interconnected with each other, neurons are able to provide efficient, lightning-fast communication. 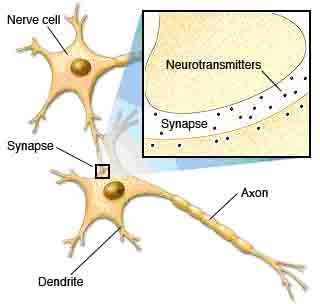 A nerve cell (neuron) communicates with other cells through electrical impulses when the nerve cell is stimulated.
Within a neuron, the impulse moves to the tip of an axon and causes the release of neurotransmitters, chemicals
that act as messengers.
A nerve cell (neuron) communicates with other cells through electrical impulses when the nerve cell is stimulated.
Within a neuron, the impulse moves to the tip of an axon and causes the release of neurotransmitters, chemicals
that act as messengers.Neurotransmitters pass through the synapse, the gap between two nerve cells, and attach to receptors on the receiving cell. This process repeats from neuron to neuron, as the impulse travels to its destination — a web of communication that allows you to move, think, feel and communicate. |
|
|
|
RGVT
|
Home
|
Determine
|
Branches
|
Que. Answer
|
IQEQSQ
|
Theory
Courses | Authorisation | About SEP | Contact Us |
|
|